33722
 Verify Ed25519 signature in Solana Anchor programThis tutorial shows how to verify off-chain Ed25519 signatures in a Solana program. In Solana, customizers typically do not implement themselves such as Ed25519 or Secp256k1 Cryptographic primitives such as signature verification, as such operations are computationally intensive and consume too many computational units in the SVM.Instead, Solana offers Ed25519Program and Secp256k1Program As a native program optimized for signature verification. This is similar to how Ethereum uses precompilation to verify ECDSA signatures, as implementing this logic directly in EVM bytecode would consume too much gas. Although wallet transactions also use Ed25519 signatures, but these signatures are verified by the Solana runtime itself, not by Ed25519Program verify. Used when you need to verify a signature contained in the transaction instruction data, such as the signature of the distributor of an airdrop claim Ed25519Program。In this article we will show how to use Ed25519Program and directive introspection to implement signature verification. Our running example will be an airdrop process where the distributor signs off-chain containing each recipient’s wallet address and token amount (recipient, amount) news. The on-chain program is responsible for distributing airdrops, it verifies these signatures to authorize token claims and will amount transferred to recipient。Ed25519Program is statelessSolana Ed25519Program performs cryptographic signature verification only based on the input parameters provided. It does not maintain any persistent data between calls, therefore, it does not own any accounts. Therefore, it does not store the results of the validation. If signature verification fails, the entire transaction will be rejected ; If successful, execution continues and the next instruction can safely assume that the signature is valid. Our running example: airdropIn an airdrop, we need a way to know who is eligible to claim tokens. One approach is to store all eligible addresses on-chain, but this is costly. Instead of storing all recipient addresses on-chain, signature-based airdrops use a trusted distributor (e.g., the project team) to sign a signature containing each recipient’s wallet address and token amount. (recipient, amount) off-chain messages. The on-chain program responsible for distributing the airdrops verifies these signatures to authorize the claim of the tokens and will amount transferred to recipient。How the verification process worksThe signature verification process uses instruction introspection, and the program can read other instructions in the same transaction. We've discussed directive introspection before, now we'll focus on how it applies to signature verification. First, our airdrop recipient submits a single transaction containing two instructions, which we will refer to in this article as** Ed25519 指令(Instruction 1) andAirdropClaim 指令**(Instruction 2):Recall that a command contains a program ID, a list of accounts, and arbitrary data interpreted by the program. We will refer to this instruction structure throughout this article: pub struct Instruction {Instruction 1: for signature verification |
| Ed25519 instruction | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| [byte 0..15] Header (16 bytes) | [Bytes 16..47] Distributor's public key (32 bytes) | [Bytes 48..111] Distributor's signature (64 bytes) | [Bytes 112..151] information – Receiver's public key (0..31) – Number of airdrop tokens (32..39, little endian) |
struct Ed25519InstructionHeader {
num_signatures: u8, // 1 字节
padding: u8, // 1 字节
offsets: Ed25519SignatureOffsets, // 14 字节
}
struct Ed25519SignatureOffsets {
signature_offset: u16, // 2 字节
signature_instruction_index: u16, // 2 字节
public_key_offset: u16, // 2 字节
public_key_instruction_index: u16, // 2 字节
message_data_offset: u16, // 2 字节
message_data_size: u16, // 2 字节
message_instruction_index: u16, // 2 字节
}Ed25519SignatureOffsets The structure has the following indexes:signature_instruction_index、public_key_instruction_index and message_instruction_index. These indexes are used to determine whether the instruction data is within the currently executing instruction. The index in the current instruction data is set to u16::MAX: let offsets = Ed25519SignatureOffsets {
signature_offset: signature_offset as u16,
signature_instruction_index: u16::MAX,
public_key_offset: public_key_offset as u16,
public_key_instruction_index: u16::MAX,
message_data_offset: message_data_offset as u16,
message_data_size: message.len() as u16,
message_instruction_index: u16::MAX,
};Ed25519 指令 The data is laid out as follows.| Ed25519 instruction | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0..15 Header (16 bytes) | 16..47 Distributor's public key | 48..111 Distributor's signature | 112..151 information – Receiver's public key (0..31) – Number of airdrop tokens (32..39, little endian) |
use solana_ed25519_program::new_ed25519_instruction_with_signature;
pub fn new_ed25519_instruction_with_signature(
message: &[u8],
signature: &[u8; 64],
pubkey: &[u8; 32],
) -> InstructionEd25519 指令 As shown below:| Ed25519 instruction | |
|---|---|
| Program ID | Ed25519SigVerify111111111111111111111111111 |
| account | [] |
| command data | – Header (signature count + offset) – Distributor's public key – Message (receiver, quantity) – Distributor's signature |
Ed25519 指令 Depend on Ed25519Program deal with. If the signature is valid, the instruction is executed successfully. However, if the signature is invalid, it aborts the transaction and logs an error code, meaning that subsequent instructions such as AirdropClaim 指令) will not be executed.AirdropClaim 指令AirdropClaim 指令 It is a standard Solana transaction instruction sent to the airdrop program to claim airdrop tokens. The command contains the airdropper ID, recipient account, and the command sysvar account for introspection. | AirdropClaim command | |
|---|---|
| Program ID | Airdrop program ID |
| account | [Receiver, directive sysvar account] |
| command data | No custom data |
Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 To verify:Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 Program ID and Ed25519Program (Ed25519SigVerify111111111111111111111111111) match.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 No account, just like no state Ed25519Program As expected.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 valid, users can claim their airdrop tokens.Ed25519 验证指令 and AirdropClaim 指令 execution processEd25519 验证指令 and AirdropClaim 指令 high-level execution process.Ed25519 验证指令 and AirdropClaim 指令。Ed25519 验证指令 Go to Ed25519Program to verify the distributor's signature.AirdropClaim 指令 Send to airdrop program.Ed25519 验证指令 Do an introspection and check its program ID, account and data to confirm it is valid Ed25519 verify.Ed25519 验证指令, users can claim their airdrop tokens.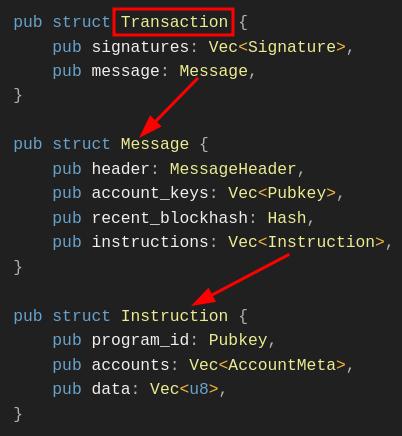
Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 and AirdropClaim 指令:指令 2, and then send the transaction to the network.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1, and allow users to claim their airdrop tokens. anchor init airdrop-distributionprograms/airdrop-distribution/lib.rs Import in file. we need to: ed25519_program import,sysvar Import for introspection.use anchor_lang::prelude::*;
use anchor_lang::solana_program::{
ed25519_program,
pubkey::Pubkey,
sysvar::instructions as ix_sysvar,
sysvar::SysvarId
};declare_iddeclare_id!("Gh2JoycvxfreSgjzhCHuRDK7sZDAbxeo7Pd8GKCoSLmS");claim Function, which contains all the logic. Here's a breakdown of what happens in the function: sysvar to read complete trading instructions.Ed25519 program and no account.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 data, then checks the header, verifies the number of signatures and extracts the offset.[recipient pubkey (32)][amount (u64 little-endian)] and check if the recipient in the signed message matches AirdropClaim 指令:指令 2 The recipient account in matches.use anchor_lang::prelude::*;
use anchor_lang::solana_program::{
ed25519_program,
pubkey::Pubkey,
sysvar::instructions as ix_sysvar,
sysvar::SysvarId
};
declare_id!("Gh2JoycvxfreSgjzhCHuRDK7sZDAbxeo7Pd8GKCoSLmS");
#[program]
pub mod airdrop {
use super::*;
pub fn claim(ctx: Context<Claim>) -> Result<()> {
// --- constants for parsing Ed25519 instruction data ---
const HEADER_LEN: usize = 16; // fixed-size instruction header
const PUBKEY_LEN: usize = 32; // size of an Ed25519 public key
const SIG_LEN: usize = 64; // size of an Ed25519 signature
const MSG_LEN: usize = 40; // expected message length: [recipient(32) + amount(8)]
// Load the instruction sysvar account (holds all tx instructions)
let ix_sysvar_account = ctx.accounts.instruction_sysvar.to_account_info();
// Index of the current instruction in the transaction
let current_ix_index = ix_sysvar::load_current_index_checked(&ix_sysvar_account)
.map_err(|_| error!(AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar))?;
// The Ed25519 verification must have run just before this instruction
require!(current_ix_index > 0, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
// Load the immediately preceding instruction (the Ed25519 ix)
let ed_ix = ix_sysvar::load_instruction_at_checked(
(current_ix_index - 1) as usize,
&ix_sysvar_account,
)
.map_err(|_| error!(AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar))?;
// Ensure it is the Ed25519 program and uses no accounts (stateless check)
require!(ed_ix.program_id == ed25519_program::id(), AirdropError::BadEd25519Program);
require!(ed_ix.accounts.is_empty(), AirdropError::BadEd25519Accounts);
// Ed25519 Verification Instruction data
let data = &ed_ix.data;
// --- parse Ed25519 instruction format ---
// First byte: number of signatures (must be 1)
// Rest of header: offsets describing where signature, pubkey, and message are
require!(data.len() >= HEADER_LEN, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
let sig_count = data[0] as usize;
require!(sig_count == 1, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
// helper to read u16 offsets from the header (little-endian)
let read_u16 = |i: usize| -> Result<u16> {
let start = 2 + 2 * i;
let end = start + 2;
let src = data
.get(start..end)
.ok_or(error!(AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar))?;
let mut arr = [0u8; 2];
arr.copy_from_slice(src);
Ok(u16::from_le_bytes(arr))
};
// Extract the offsets for signature, pubkey, and message
let signature_offset = read_u16(0)? as usize;
let signature_ix_idx = read_u16(1)? as usize;
let public_key_offset = read_u16(2)? as usize;
let public_key_ix_idx = read_u16(3)? as usize;
let message_offset = read_u16(4)? as usize;
let message_size = read_u16(5)? as usize;
let message_ix_idx = read_u16(6)? as usize;
// Enforce that all offsets point to the current instruction's data.
// The Ed25519 program uses u16::MAX as a sentinel value for "current instruction".
// This prevents the program from accidentally reading signature, public key,
// or message bytes from some other instruction in the transaction.
let this_ix = u16::MAX as usize;
require!(
signature_ix_idx == this_ix
&& public_key_ix_idx == this_ix
&& message_ix_idx == this_ix,
AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar
);
// Ensure all offsets point beyond the 16-byte header,
// i.e. into the region containing the signature, public key, and message
require!(
signature_offset >= HEADER_LEN
&& public_key_offset >= HEADER_LEN
&& message_offset >= HEADER_LEN,
AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar
);
// Bounds checks for signature, pubkey, and message slices
require!(data.len() >= signature_offset + SIG_LEN, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
require!(data.len() >= public_key_offset + PUBKEY_LEN, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
require!(data.len() >= message_offset + message_size, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
require!(message_size == MSG_LEN, AirdropError::InvalidInstructionSysvar);
// --- reconstruct and validate the distributor's pubkey ---
let pk_slice = &data[public_key_offset..public_key_offset + PUBKEY_LEN];
let mut pk_arr = [0u8; 32];
pk_arr.copy_from_slice(pk_slice);
let distributor_pubkey = Pubkey::new_from_array(pk_arr);
if distributor_pubkey != ctx.accounts.expected_distributor.key() {
return err!(AirdropError::DistributorMismatch);
}
// --- reconstruct and validate the signed message ---
// Format: [recipient pubkey (32 bytes)][amount (u64 little-endian)]
let msg = &data[message_offset..message_offset + message_size];
let mut rec_arr = [0u8; 32];
rec_arr.copy_from_slice(&msg[0..32]);
let recipient_from_msg = Pubkey::new_from_array(rec_arr);
if recipient_from_msg != ctx.accounts.recipient.key() {
return err!(AirdropError::RecipientMismatch);
}
let mut amount_bytes = [0u8; 8];
amount_bytes.copy_from_slice(&msg[32..40]);
let amount = u64::from_le_bytes(amount_bytes);
// User can now claim the airdrop token.
// The airdrop transfer can now be implemented here.
Ok(())
}
}
#[derive(Accounts)]
pub struct Claim<'info> {
/// The recipient of the airdrop (must match the recipient in the signed message)
#[account(mut)]
pub recipient: Signer<'info>,
/// Expected distributor pubkey (checked against signed message, not Anchor)
/// CHECK: Validated manually against the parsed message
pub expected_distributor: UncheckedAccount<'info>,
/// The sysvar containing the full transaction's instructions
/// CHECK: Validated by requiring its well-known address
#[account(address = ix_sysvar::Instructions::id())]
pub instruction_sysvar: AccountInfo<'info>,
/// System program used for the transfer
pub system_program: Program<'info, System>,
}
#[error_code]
pub enum AirdropError {
#[msg("Invalid instruction sysvar")]
InvalidInstructionSysvar,
#[msg("Expected Ed25519 program id")]
BadEd25519Program,
#[msg("Bad Ed25519 accounts")]
BadEd25519Accounts,
#[msg("Distributor public key mismatch")]
DistributorMismatch,
#[msg("Recipient mismatch in message")]
RecipientMismatch,
}Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 dataEd25519 验证指令:指令 1Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1。load_current_index_checked() to get the index of the current instruction and call load_instruction_at_checked() to load the immediately previous instruction.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1),us:Ed25519Program match. This ensures that the instruction is indeed an Ed25519 signature verification. data。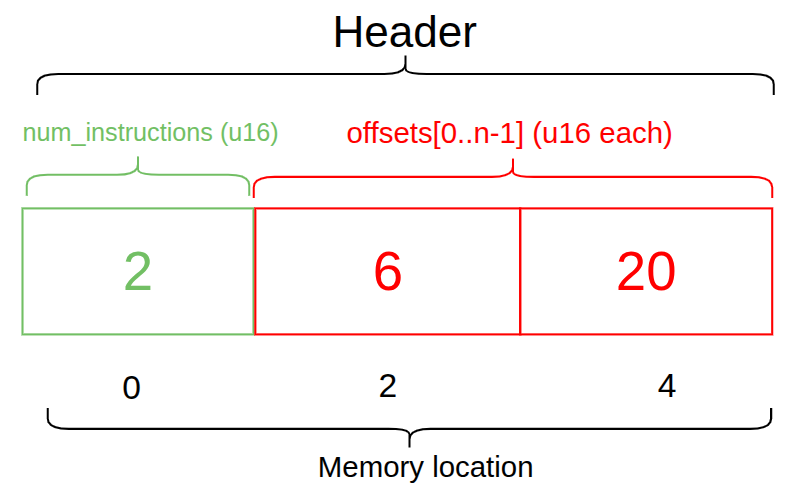
ed2559Program Command information: ID and account. We also obtained Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 data, so the next step is to verify the contents of the data. The data is u8 Vector of data type.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 data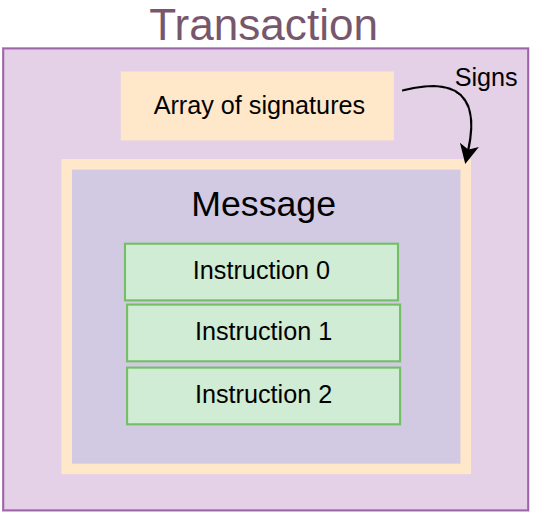
Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 data.Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 The signature count, offset, and index to the location of each element are extracted from the data vector.data[0] Get the index. The expected count is 1 since there should only be one distributor signing. we use require statement enforces this requirement.read_u16, which iterates over the data buffer 2 bytes at a time and takes each offset as u16 return. This makes it easier to recreate a consistent instruction data layout. 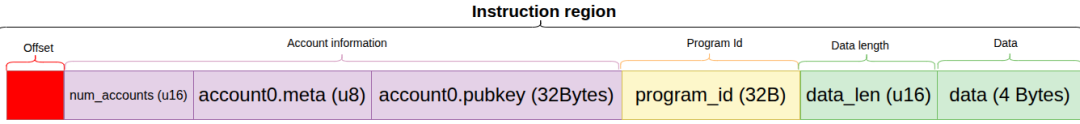
signature_ix_idx), public key (public_key_ix_idx) and messages (message_ix_idx) in the Ed25519 source code is set to u16::MAX. Any other value will point to another instruction in the transaction. 
Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 The offsets parsed by the data header are used to locate the distributor's public key and message content (recipient and amount) in the instruction data, and are determined based on the user's AirdropClaim 指令:指令 2 Verify the version provided in .Ed25519 指令 Cut out the distributor's public key from the data and reconstruct it into a 32-byte Pubkey, and combine it with AirdropClaim 指令:指令 2 in the distributor account expected_distributor Public keys are compared.AirdropClaim 指令:指令 2 in recipient Account matches.
Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1 and AirdropClaim 指令:指令 2) transaction to test it.tweetnacl cryptographic library to create distributor signatures, so install it by running the following command:yarn add tweetnacltweetnacl add to tests/airdrop-distribution.ts in the import as shown below. we will use Ed25519Program dependencies to create the first directive for verification, while TransactionInstruction is the expected standard trading order type.import * as anchor from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { Program } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { expect } from "chai";
// Add the following
import { Airdrop } from "../target/types/airdrop"; // The IDL
import {
PublicKey,
Keypair,
SystemProgram,
Transaction,
**TransactionInstruction,
Ed25519Program**
} from "@solana/web3.js";
import * as nacl from "tweetnacl";Ed25519Program The command is in claim The order is front-running, and the transaction is successful.claim The command is in Ed25519Program Before, the transaction failed and appeared InvalidInstructionSysvar mistake.expectedDistributor Signature does not match, transaction fails, appears DistributorMismatch mistake.RecipientMismatch mistake.AirdropClaim 指令 Attempts to trick the system will fail. This is because the program's introspection logic only looks at the immediately preceding Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1, so the second AirdropClaim 指令 will fail.// ...
describe("airdrop", () => {
// Configure the client to use the local cluster
anchor.setProvider(anchor.AnchorProvider.env());
const program = anchor.workspace.Airdrop as Program<Airdrop>;
const provider = anchor.getProvider();
// Test accounts
let distributorKeypair: Keypair;
let recipientKeypair: Keypair;
let invalidDistributorKeypair: Keypair;
before(async () => {
// Generate test keypairs
distributorKeypair = Keypair.generate();
recipientKeypair = Keypair.generate();
invalidDistributorKeypair = Keypair.generate();
});
Ed25519 验证指令:指令 1. It builds the message from the recipient and amount, signs it with the distributor's key, and then uses Ed25519Program.createInstructionWithPublicKey Returns something that can be verified at runtime TransactionInstruction。function createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair: Keypair,
recipientPubkey: PublicKey,
amount: number
): TransactionInstruction {
// Build the message: 32 bytes recipient pubkey + 8 bytes amount
const message = Buffer.alloc(40);
recipientPubkey.toBuffer().copy(message, 0);
message.writeBigUInt64LE(BigInt(amount), 32);
// Sign the message with distributor
const signature = nacl.sign.detached(message, distributorKeypair.secretKey);
// Use the helper to build the instruction
return Ed25519Program.createInstructionWithPublicKey({
publicKey: distributorKeypair.publicKey.toBytes(),
message,
signature,
});
}
```我们将在我们的测试用例中重用上述函数来创建 `Ed25519 Verification Instruction: Instruction 1`。让我们从我们的第一个测试用例开始,这是一个有效的空投声明,应该成功。
我们创建两个指令:`Ed25519 Verification Instruction: Instruction 1` 和 `AirdropClaim Instruction: Instruction 2`。我们将 distributor、recipient 和 instruction sysvar 账户传递给程序的 `claim` 函数,如前所述。然后我们发送交易并确认它成功。成功时,它返回一个交易 ID;否则,我们会收到一个错误。
```tsx hljs language-typescript
it("Successfully claims airdrop with valid signature", async () => {
const claimAmount = 1000000;
// Create Ed25519 Signature Verification Instruction: Instruction 1
const ed25519Ix = createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair,
recipientKeypair.publicKey,
claimAmount
);
// Create the AirdropClaim Instruction: Instruction 2
const claimIx = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey,
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
const tx = new Transaction();
tx.add(ed25519Ix); // Add Instruction 1 to the transaction
tx.add(claimIx); // Add Instruction 2 to the transaction
// Just expect the transaction to succeed
expect(await provider.sendAndConfirm(tx, [recipientKeypair])).to.not.be.empty;
});import * as anchor from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { Program } from "@coral-xyz/anchor";
import { Airdrop } from "../target/types/airdrop";
import { PublicKey, Keypair, SystemProgram, Transaction, TransactionInstruction, Ed25519Program } from "@solana/web3.js";
import { expect } from "chai";
import * as nacl from "tweetnacl";
describe("airdrop", () => {
// Configure the client to use the local cluster
anchor.setProvider(anchor.AnchorProvider.env());
const program = anchor.workspace.Airdrop as Program<Airdrop>;
const provider = anchor.getProvider();
// Test accounts
let distributorKeypair: Keypair;
let recipientKeypair: Keypair;
let invalidDistributorKeypair: Keypair;
before(async () => {
// Generate test keypairs
distributorKeypair = Keypair.generate();
recipientKeypair = Keypair.generate();
invalidDistributorKeypair = Keypair.generate();
});
function createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair: Keypair,
recipientPubkey: PublicKey,
amount: number
): TransactionInstruction {
// Build the message: 32 bytes recipient pubkey + 8 bytes amount
const message = Buffer.alloc(40);
recipientPubkey.toBuffer().copy(message, 0);
message.writeBigUInt64LE(BigInt(amount), 32);
// Sign the message with distributor
const signature = nacl.sign.detached(message, distributorKeypair.secretKey);
// Use the helper to build the instruction
return Ed25519Program.createInstructionWithPublicKey({
publicKey: distributorKeypair.publicKey.toBytes(),
message,
signature,
});
}
it("Successfully claims airdrop with valid signature", async () => {
const claimAmount = 1000000;
const ed25519Ix = createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair,
recipientKeypair.publicKey,
claimAmount
);
const claimIx = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey,
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
const tx = new Transaction();
tx.add(ed25519Ix);
tx.add(claimIx); // AirdropClaim Instruction: Instruction 2
// Just expect the transaction to succeed
expect(await provider.sendAndConfirm(tx, [recipientKeypair])).to.not.be.empty;
});
it("Fails when Ed25519 instruction is not first", async () => {
const claimAmount = 1000000;
const claimIx = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey,
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
const ed25519Ix = createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair,
recipientKeypair.publicKey,
claimAmount
);
// Create transaction with claim first, then Ed25519 (wrong order)
const tx = new Transaction();
tx.add(claimIx);
tx.add(ed25519Ix);
try {
await provider.sendAndConfirm(tx, [recipientKeypair]);
expect.fail("Should have failed with wrong instruction order");
} catch (error) {
expect(error.message).to.include("InvalidInstructionSysvar");
}
});
it("Fails with distributor mismatch", async () => {
const claimAmount = 1000000;
// Create Ed25519 instruction with wrong distributor
const ed25519Ix = createEd25519Instruction(
invalidDistributorKeypair, // Wrong distributor signs
recipientKeypair.publicKey,
claimAmount
);
const claimIx = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey, // But we expect the correct one
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
const tx = new Transaction();
tx.add(ed25519Ix);
tx.add(claimIx);
try {
await provider.sendAndConfirm(tx, [recipientKeypair]);
expect.fail("Should have failed with distributor mismatch");
} catch (error) {
expect(error.message).to.include("DistributorMismatch");
}
});
it("Fails with recipient mismatch", async () => {
const claimAmount = 1000000;
const wrongRecipient = Keypair.generate();
// Create Ed25519 instruction with wrong recipient in message
const ed25519Ix = createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair,
wrongRecipient.publicKey, // Wrong recipient in signed message
claimAmount
);
const claimIx = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey,
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
const tx = new Transaction();
tx.add(ed25519Ix);
tx.add(claimIx);
try {
await provider.sendAndConfirm(tx, [recipientKeypair]);
expect.fail("Should have failed with recipient mismatch");
} catch (error) {
expect(error.message).to.include("RecipientMismatch");
}
});
it("Fails when multiple claim instructions try to reuse the same Ed25519 signature", async () => {
const claimAmount = 1000000;
// Create a single Ed25519 instruction
const ed25519Ix = createEd25519Instruction(
distributorKeypair,
recipientKeypair.publicKey,
claimAmount
);
// First claim instruction (valid)
const claimIx1 = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey,
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
// Second claim instruction (tries to reuse the same Ed25519)
const claimIx2 = await program.methods
.claim()
.accountsPartial({
recipient: recipientKeypair.publicKey,
expectedDistributor: distributorKeypair.publicKey,
instructionSysvar: anchor.web3.SYSVAR_INSTRUCTIONS_PUBKEY,
})
.instruction();
const tx = new Transaction();
tx.add(ed25519Ix);
tx.add(claimIx1);
tx.add(claimIx2);
try {
await provider.sendAndConfirm(tx, [recipientKeypair]);
expect.fail("Should have failed because multiple claims tried to reuse the same signature");
} catch (error) {
// The second claim fails because its immediately preceding instruction
// is not the Ed25519 verification, so the program throws
expect(error.message).to.include("BadEd25519Program");
}
});
});anchor test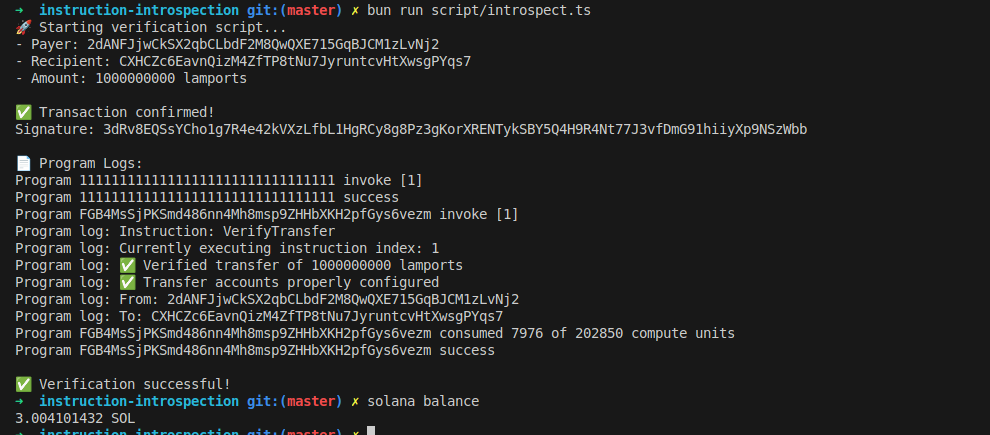
- Original link: https://rareskills.io/post/solana-signature-verification
- Denglian community AI assistant translates excellent English articles for everyone. If there are any incomprehensible translations, please forgive me~


